We delve into experiential learning and the transformative approach of learning through direct experience, known as experiential learning. This article explores the fundamental aspects of this educational method, including its principles, benefits, and the challenges in its implementation. Additionally, we examine the significant role of technology in enriching these learning experiences.
Key Takeaways
- Essence of Experiential Learning: Definition and evolution of experiential learning, contrasting it with traditional educational methods.
- Core Principles: Exploration of key principles like learning through experience, reflection, and application, including David Kolb’s Experiential Learning Model.
- Benefits Unveiled: Insight into how experiential learning enhances critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and bridges the gap between theory and practice.
- Technology’s Impact: Discussion on how digital advancements like e-learning and virtual reality are revolutionizing experiential learning.
Table of Contents
- What is Experiential Learning?
- Principles of Experiential Learning
- Benefits of Experiential Learning
- Challenges and Considerations
- Experiential Learning in the Digital Age: The Role of Technology
- Appsembler and Experiential Learning
- Implementing Experiential Learning Strategies
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Experiential Learning?
Experiential learning, an educational philosophy rooted in learning through experience, stands as a dynamic contrast to the traditional, theory-centric methods prevalent in most classrooms. This approach is founded on the principle that knowledge is formed through the transformation of experience. It emphasizes ‘doing’ rather than just ‘listening’ or ‘observing’, fostering a deeper understanding through active engagement and reflection.
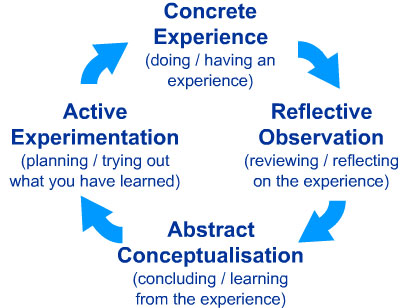
The roots of experiential learning trace back to several educational theorists, most notably John Dewey, Jean Piaget, and Kurt Lewin. Dewey, in his seminal work “Experience and Education” (1938). David A. Kolb developed these theories into a comprehensive model in the 1970s. His Experiential Learning Model (ELM) proposed that learning is a process where knowledge is created through a transformation of experience. This model emphasizes four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. These stages create a continuous learning cycle, where each phase is equally important.
The evolution of experiential learning theory has significantly influenced educational practices. Today, it is not confined to physical experiences alone; with the advent of Learning Management Systems (LMS) and Virtual Labs, experiential learning has transcended traditional boundaries. These digital platforms provide simulated environments where learners can engage in realistic scenarios, enhancing their learning experience beyond the conventional classroom setting.
In sum, experiential learning is a holistic approach that combines action, reflection, theory, and practice. It acknowledges that learning is a personal and interactive process and adapts to the evolving educational landscape, making it a vital methodology in contemporary education.
Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning pivots on core principles that distinguish it from traditional learning paradigms. These principles—learning through experience, reflection, and application—are foundational to understanding and effectively implementing this educational approach.
Learning Through Experience: This principle posits that learning is most effective when learners are directly involved in a hands-on experience. Unlike passive learning, which often involves listening to lectures or reading textbooks, experiential learning encourages students to engage actively with the material, fostering a deeper understanding. Experiential learning could involve anything from participating in a lab experiment to embarking on a field study. The key is that learners are not mere spectators but active participants in their learning journey.
Reflection: Reflection is a critical component of experiential learning. It involves learners thinking critically about their experiences, analyzing what they did, how they did it, and what they learned from it. This reflective process enables them to connect theoretical knowledge with practical application. It encourages self-assessment and helps internalize the learning, ensuring that the experience transcends being just an activity.
Application: The third principle is the application, which involves using the newly acquired knowledge or skills in real-world scenarios. This might involve solving practical problems, creating new projects, or applying concepts in different contexts. The application ensures that the learning is not just theoretical but has practical utility and relevance.
In the heart of these principles lies David Kolb’s Experiential Learning Model (ELM), a pivotal framework in understanding experiential learning. Kolb’s model outlines a four-stage learning process:
- Concrete Experience: In this type of learning, students actively engage in an experience, such as a lab experiment, fieldwork, or group project.
- Reflective Observation: In this stage, learners reflect on the experience. They observe what happened and analyze their reactions and the outcomes.
- Abstract Conceptualization: Learners use their reflections to develop new ideas or modify existing concepts. This stage involves critical thinking and conceptualization.
- Active Experimentation: Finally, learners apply their new understanding in different situations, experimenting with new ways of doing things.
Kolb’s model suggests that learning is a continuous process that cycles through these stages. It emphasizes that experiences alone are insufficient for learning; they must be accompanied by reflection, conceptualization, and application. This model has profoundly influenced how educators and institutions design and implement learning experiences, ensuring that they cater to the holistic development of learners.
The learning environment and context play significant roles in experiential learning. The environment must be conducive to exploration, experimentation, and critical thinking. Whether it’s a physical classroom, a virtual lab, or an outdoor setting, the environment should be aligned with the objectives of the learning experience, providing a safe and supportive space for learners to experiment, fail, and learn.
The principles of experiential learning emphasize active participation, reflection, conceptualization, and application, all within a supportive learning environment. These principles underpin experiential learning’s transformative power, making it an effective approach to education in the 21st century.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning, with its emphasis on active participation and reflection, offers a multitude of benefits that enhance both personal and professional development. Among its most significant advantages are enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, improving interpersonal and communication skills, bridging the gap between theory and practice, and fostering long-term retention and deeper understanding of subject matter.
Enhancing Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills: Experiential learning places learners in real-world scenarios where they must navigate challenges and make decisions. This process naturally cultivates critical thinking as learners assess situations, weigh options, and foresee consequences. Problem-solving skills are honed as students learn to identify issues, develop strategies, and apply solutions in practical settings. These skills are invaluable in today’s fast-paced, ever-changing world.
Improving Interpersonal and Communication Skills: Interactions with peers, mentors, and professionals in experiential learning settings are opportunities to develop interpersonal skills. Working in teams, negotiating, and resolving conflicts are common experiences that enhance learners’ ability to communicate effectively and work collaboratively. These skills are essential in any professional environment, making learners better prepared for their careers.
Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice: Experiential learning effectively bridges the often-cited gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. By engaging in hands-on activities, learners can see how abstract concepts are applied in real-world situations, enhancing their understanding and appreciation of the subject matter.
Long-Term Retention and Deeper Understanding of Subject Matter: Experiential learning’s active nature promotes more profound engagement with the material, leading to better understanding and longer retention of information. When learners actively participate in the learning process, they are more likely to remember and internalize the knowledge gained. This deeper understanding aids in academic performance and applying knowledge in future careers.
In summary, experiential learning is a multifaceted approach that equips learners with essential skills and knowledge and prepares them for real-world challenges, fostering both personal growth and professional readiness.
Challenges and Considerations
While experiential learning offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own challenges and considerations that educators and institutions must address to ensure its effective implementation.
Balancing Experiential and Traditional Learning Methods: One of the primary challenges is finding the right balance between experiential and traditional learning. While experiential learning is invaluable, traditional methods like lectures and textbooks still play a crucial role in providing foundational knowledge. Striking a balance that leverages the strengths of both approaches is essential. This requires careful curriculum planning to ensure that experiential activities complement and reinforce theoretical learning.
Addressing Resource Constraints and Logistical Issues: Experiential learning often demands more resources than traditional classroom-based education. Whether setting up lab equipment, organizing field trips, or arranging internships, these activities can be resource-intensive. Additionally, logistical issues such as scheduling, coordination with external partners, and managing group dynamics pose significant challenges. Institutions must plan meticulously and allocate resources effectively to overcome these hurdles.
Ensuring Safety and Ethical Considerations in Experiential Settings: Safety is paramount in experiential learning environments, especially in physical tasks or fieldwork activities. Educators must ensure that safety protocols are in place and adhered to. Moreover, ethical considerations are critical, particularly in service learning and community engagement. Respect for community partners and sensitivity to the needs and cultures of those served is essential for ethical experiential learning.
Customizing Experiences to Diverse Learning Styles and Needs: Finally, experiential learning must be inclusive and accommodating of diverse learning styles and needs. Not all students benefit from the same types of experiences. Some may thrive in hands-on environments, while others might find reflective observation more beneficial. Tailoring experiences to meet these varied needs and learning styles can be challenging but is crucial for an inclusive educational experience.
While experiential learning is a powerful educational tool, it requires careful consideration of balance, resources, safety, ethics, and inclusivity. Addressing these challenges is key to creating effective, enriching, and safe learning experiences for all students.
Experiential Learning in the Digital Age: The Role of Technology
Technology plays a pivotal role in reshaping and enhancing experiential learning in the digital age. Tools like e-learning platforms and virtual reality (VR) have expanded the horizons of experiential learning, while social media and collaborative platforms have introduced new dimensions of interaction and engagement.
E-Learning and Virtual Reality as Tools for Experiential Learning: E-learning platforms have made learning more accessible, providing interactive and immersive experiences beyond traditional classroom boundaries. These platforms facilitate various experiential activities, from online simulations to interactive assignments, allowing learners to explore and apply concepts in virtual settings. Virtual reality takes this a step further by offering fully immersive experiences. VR technology can simulate complex environments and scenarios, from medical procedures to historical events, providing learners with a safe space to practice and hone their skills without the constraints of the physical world.
The Impact of Social Media and Collaborative Platforms: Social media and collaborative platforms have emerged as significant tools in experiential learning. They provide a space for learners to connect, share experiences, and collaborate on projects, transcending geographical barriers. These platforms facilitate peer-to-peer learning and community building, enabling learners to engage in discussions, share insights, and receive feedback from a global community. They also allow for creating digital portfolios, where students can showcase their work and learning journey.
Technology has significantly expanded the scope and accessibility of experiential learning. E-learning, VR, social media, and collaborative platforms enhance learning experiences and prepare students for a technology-driven world, making them adaptable and proficient in digital tools and platforms.
Appsembler and Experiential Learning
Appsembler specializes in offering customizable, scalable, and user-friendly online learning platforms. Its primary offering, Tahoe LMS, is a powerful LMS that allows educators and organizations to create and manage online courses effectively. Tahoe LMS is known for its flexibility, enabling the integration of various interactive elements such as videos, quizzes, and discussion forums, which are essential for a dynamic learning experience.
How Appsembler Facilitates Experiential Learning: Appsembler’s platform excels in providing real-world, hands-on learning experiences through Virtual Labs and interactive course content. These virtual labs allow learners to practice skills in a simulated environment that mimics real-life scenarios, bridging the gap between theory and application. The platform’s interactive nature encourages active learning and engagement, essential components of the experiential learning process.
In essence, Appsembler’s Tahoe LMS and Virtual Labs serve as a bridge, connecting theoretical knowledge with practical application. It is a testament to technology’s potential to revolutionize experiential learning.
Implementing Experiential Learning Strategies
Implementing experiential learning strategies requires careful planning and execution. Educators and institutions seeking to incorporate these strategies must consider several critical steps and best practices to ensure effective and meaningful learning experiences.
Steps for Educators and Institutions to Incorporate Experiential Learning:
- Needs Assessment: Begin with a thorough assessment of students’ needs and learning objectives. Understanding the learners’ profiles and desired outcomes is crucial in designing relevant experiential learning activities.
- Integrating with Curriculum: Experiential learning activities should complement and enhance the existing curriculum. Aligning these activities with course objectives ensures that they reinforce theoretical concepts and provide practical applications.
- Resource Allocation: Identify and allocate the necessary resources, including technology, materials, and personnel. This may involve investing in new technologies like VR for simulation-based learning or collaborating with external organizations for internships.
- Training and Professional Development: Educators should be trained in experiential learning methodologies. Professional development programs can equip them with the skills and knowledge to facilitate and guide experiential learning effectively.
Best Practices for Designing and Executing Experiential Learning Activities:
- Authenticity: Ensure that the experiences are authentic and relevant to real-world scenarios. Authentic experiences are more engaging and meaningful to learners.
- Reflection and Debriefing: Incorporate structured reflection and debriefing sessions. These are crucial for learners to process their experiences and derive insights and learning points.
- Diversity and Inclusivity: Design activities that cater to diverse learning styles and needs, ensuring inclusivity and accessibility for all learners.
- Feedback and Support: Provide continuous feedback and support throughout the experiential learning process. Constructive feedback guides learners and enhances their learning experience.
Evaluating and Measuring the Effectiveness of Experiential Learning:
- Assessment Techniques: To gauge learners’ progress, use various assessment techniques, including self-assessments, peer reviews, and performance evaluations.
- Outcome Measurement: Measure outcomes against predefined objectives. This could include qualitative and quantitative data, such as skill development, concept mastery, and behavioral changes.
- Continuous Improvement: Use the insights from evaluations for continuous improvement of the experiential learning activities. Feedback from learners and educators should inform future iterations and enhancements.
Implementing experiential learning strategies requires a strategic approach, focusing on relevance, alignment with curriculum, and effective facilitation. Through careful planning, execution, and evaluation, experiential learning can become a transformative tool in education, providing learners with valuable skills and insights for personal and professional development.
Conclusion
As we explore the landscape of education, it’s evident that experiential learning is not merely a fleeting trend but a fundamental shift in how we approach teaching and learning. The key takeaways from this exploration underscore the immense value of experiential learning: its ability to enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills, its efficacy in bridging theory with practical application, and its role in preparing learners for real-world challenges.
As educators, learners, and institutions, embracing experiential learning means being at the forefront of educational innovation. It involves committing to a learning approach that is dynamic, interactive, and deeply rooted in real-world experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Experiential learning distinguishes itself from traditional learning by emphasizing hands-on, practical experiences over passive absorption of information. While traditional education often relies on lectures, readings, and rote memorization, experiential learning involves active engagement with the material. It requires students to apply their knowledge in real-world situations, reflect on these experiences, and adapt their understanding based on these reflections. This approach leads to deeper comprehension, better retention of knowledge, and the development of practical skills that are directly applicable to real-life scenarios.
Absolutely. Experiential learning can be effectively incorporated into online education through various digital tools and platforms. Virtual simulations, interactive assignments, and collaborative projects enable students to engage in experiential learning remotely. E-learning platforms, augmented reality, and virtual reality technologies have opened new avenues for experiential learning, making it more accessible and versatile. These tools allow students to gain practical experience in a virtual environment, ensuring that the essence of experiential learning is maintained even in an online setting.
Experiential learning activities can vary widely, including internships, apprenticeships, field trips, study abroad programs, service learning, community engagement projects, and simulation-based learning. These activities allow students to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, whether it’s in a professional workplace, a cultural immersion in a foreign country, or a virtual simulation environment. Each type of activity provides unique opportunities for hands-on learning and skill development.
Experiential learning significantly enhances skill development by providing real-world contexts in which students can practice and refine their abilities. It improves not only technical skills specific to a field of study but also transferrable skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, communication, and teamwork. By engaging students in practical experiences and reflective practices, experiential learning ensures that they develop both the hard and soft skills necessary for personal and professional success.